Digital Wallet Cybercrime is the Next Target to Watch

Rising interest of threat actors in digital wallets may have affected trade of stolen credit cards on dark web markets
The use of digital wallets is on the rise and is likely to continue to grow and supplant credit cards as the payment method of choice for online purchases. Since the start of the Covid-19 pandemic, there has been a 6.5% increase in the use of digital wallets on online sites. The number of interactions of threat actors on the Dark Web related to the illicit use of digital wallets, digital wallet exploits, cybercrime, and fraud has skyrocketed.
How are cyber criminals profiting from digital wallets?
While examining its popularity among cybercriminals, our study on digital wallets found that threat actors commonly use digital wallets as a way of paying for the sale of illegal products. The study also found that threat actors have several intentions in the context of digital wallets:
- Methods and tutorials – a large number of publications of methods or tutorials of how to hack digital wallets were published on Dark Web platforms. Most of the posts sell these tutorials for a profit, at prices ranging from $25 to more than $150. The methods mostly use digital wallets as a conduit to transfer money from a stolen credit card to an easy-to-use platform. One popular technique is to purchase gift cards with the wallet as a way of laundering money.
- Verifying digital wallet accounts – another common trend we came across was the sale of verification services on the Dark Web that allowed an attacker to impersonate a user to satisfy requests to verify accounts. To transfer money from a credit card, the account needs to be verified with a detailed process that is required for a user to withdraw more than $500 from an account.
- Sale of vulnerabilities – one developing trend is the trade of vulnerabilities found in digital wallets. Our study found vulnerabilities in Apple Pay, Samsung Pay and Google Pay posted for sale on one of the forums monitored.
- Phishing – digital wallets are becoming more vulnerable to phishing, one of the most popular vectors for attack. Threat actors manipulate users to enter a malicious link or file pretending to belong to a legitimate wallet in order to expose their credentials.
As expected, the online discourse is increasing alongside the growth in the use of payment applications. While still in its infancy, it is expected that digital wallet-related cybercrime will become as popular as other financial cybercrimes, with digital wallets becoming a prime target of different threat actors.
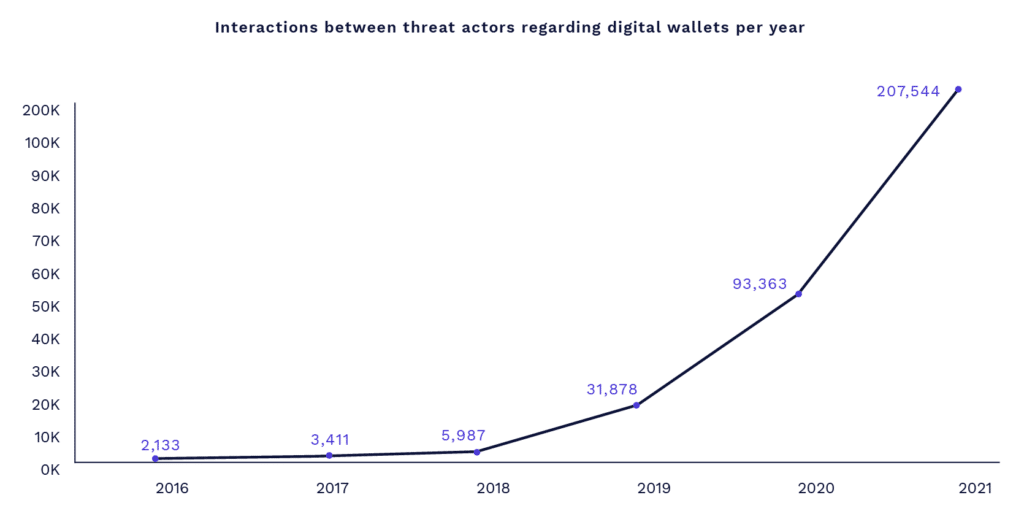
The Cognyte Cyber Threat Intelligence team gathered and analyzed the number of interactions by threat actors regarding digital wallets between 2016-2020. These interactions included questions asked by threat actors, hacking tutorials, wallets mentioned as a payment method, etc., and were particularly applicable to Google Pay, Apple Pay, and Samsung Pay. A variety of sources were analyzed, including Telegram, Twitter, underground hacking forums, and Darknet markets.
The below graph illustrates the continuous upward trend in the number of interactions, which almost doubled from 2017 to 2018, and experienced a 5-fold increase in 2019, reaching 31,878 interactions. In 2020 the interactions reached 96,363 and in 2021, there were more than 200,000 interactions. We forecast that the topic will remain hot this year and will increase in line with the growth of digital wallets usage globally.
How is the rise of digital wallets affecting credit card fraud?
While illicit interactions surrounding digital wallets have increased in line with their use, we noticed that the trend of selling credit cards on Dark Web markets is slowing dramatically. When examining data collected from 50 credit card shops on the Dark Web, our analysis revealed a decline of 24.5% in the sale of credit card numbers from 2019 to 2020. This may indicate that threat actors are moving to other attack methods, such as digital wallet cybercrime.
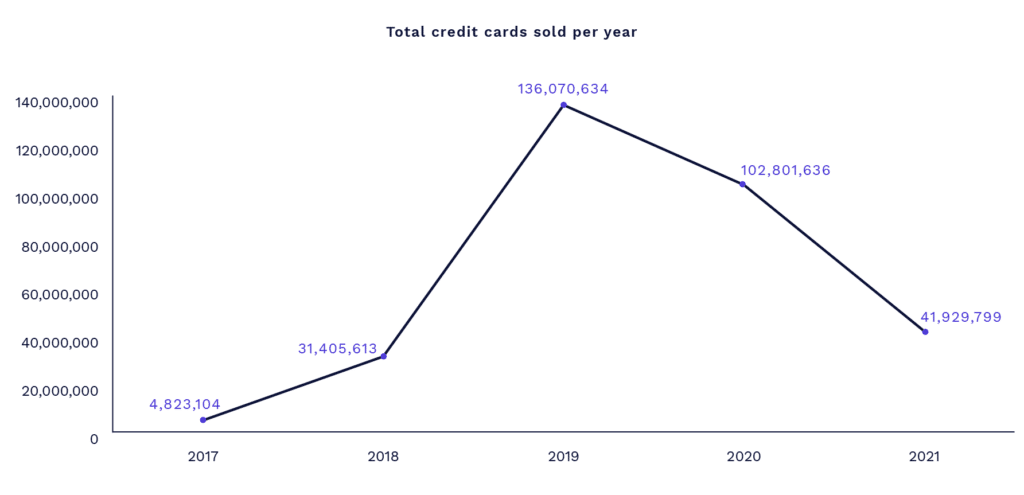
Digital wallet credential theft is supplanting credit card fraud due in part to the increasing popularity of digital wallets. Criminals are trending toward the mass sale of credentials through databases marketed on the Dark Web and are subsequently committing fraud and unauthorized purchases using the wallets or associated credit cards.
What does the increase of digital wallet cybercrime mean for financial institutions?
Financial institutions are affected by the theft of digital wallet credentials in the same way as traditional credit card theft since digital wallets are typically connected to credit cards. Leaks of stolen digital wallet credentials can become credit card data breaches and can threaten customer trust in the security of their financial service providers and harm their reputations. Even if credit card data is not leaked, fraudulent purchases may be made, requiring financial service providers to compensate fraud victims.
As the payment ecosystem shifts toward digital wallets, financial institutions may be expected to provide digital wallets as a service. Getting ahead of potential security breaches will be essential for financial service providers to keep up with this evolving market trend.
Cognyte can help you detect threats to customers’ digital wallets
Cognyte’s Cyber Threat Intelligence Solution, LUMINAR, continuously monitors all layers of the web to provide tailored, real-time alerts whenever threat actors attempt to trade credit card or digital wallet credentials. LUMINAR’s dedicated fraud module enables users to discover credentials tied to your specific customers as soon as someone exposes them. Advanced analytics, a proprietary database and IOC capabilities trace attackers’ historic activities, even in defunct forums, to correlate ongoing patterns and identify criminals. Now you can improve your security posture by identifying threats to your customers’ security before they strike.
Click here to read the full report: Digital Wallets in the Cyber World.