What is Criminal Investigative Analysis?

Criminal Investigative Analysis
Criminal investigative analysis, also known as criminal profiling, is a technique used by law enforcement agencies to identify the characteristics of an unknown criminal offender based on data collected in the course of the investigation as well as evidence left at the crime scene. The technique has been used since the 19th century1, but it gained popularity in the 1970s after the FBI’s Behavioral Science Unit (BSU) started using it to solve high-profile cases. According to the FBI, criminal investigative analysis has helped solve more than 6,000 cases since its inception2. Criminal investigative analysis has also been popularized in movies and TV shows such as “The Silence of the Lambs” and “Mindhunter”3. In this blog post, we will explore criminal investigative analysis and how it can be enhanced with new technological capabilities.
What is Criminal Investigative Analysis?
The primary objective of criminal investigative analysis is to provide a psychological and behavioral assessment of the offender, drawing insights from evidence at crime scenes and observed patterns in their criminal behavior. This multidisciplinary analytical procedure involves organizing and analyzing data, aiding investigators in cases of serial crimes where patterns emerge over multiple incidents. It also helps in narrowing down a potential list of suspects, based on patterns and evidence revealed during the investigation process.
Practitioners may differ in methodologies and terminology, yet they share a common goal of analyzing data to develop a profile of an unknown offender.
Attributes of an offender profile may include:
- Antisocial personality traits
- Psychopathologies
- Behavioral patterns
- Demographic variables: age, geographic location, family status, etc.
[Source: APA Monitor on Psychology, 2004]
The Need for Criminal Investigative Analysis
Criminal investigative analysis is critical in solving many crimes, especially complex or hard-to-solve cases. Without the aid of criminal investigative analysis, investigations are less efficient, exhaust more resources, and are characterized by a scattershot approach to pursuing leads. The absence of a systematic and behavioral assessment approach often results in a time-consuming investigative process, where law enforcement navigates a myriad of potential leads without the targeted insights that criminal investigative analysis can provide.

How Do Law Enforcement Agencies Typically Use Criminal Investigative Analysis?
Criminal investigative analysis is often used in cases involving serial crimes, such as murders or sexual assaults, where patterns and behaviors may emerge over multiple incidents. Profilers use their expertise to assist investigators in prioritizing leads, understanding the offender’s mindset, and developing strategies for apprehension.
Profilers rely on their experience, knowledge of criminal behavior, and a careful analysis of available data to provide assistance to law enforcement agencies.
The Criminal Investigative Analysis Process
Criminal investigative analysis plays a crucial role across the investigation, apprehension, and prosecution phases of the criminal justice process. During the investigation phase, profilers analyze all available data to uncover patterns or links between victims or between criminal incidents, predict the personality traits and behaviors of unknown perpetrators, and formulate strategies for apprehension. In the apprehension phase, profiling is instrumental in predicting locations, determining search warrant criteria, and anticipating the reactions of an unidentified serial criminal upon capture. In the prosecution phase, criminal profilers serve as expert witnesses in court, utilizing investigative data to establish connections between crimes and link alleged perpetrators to a series of offenses.
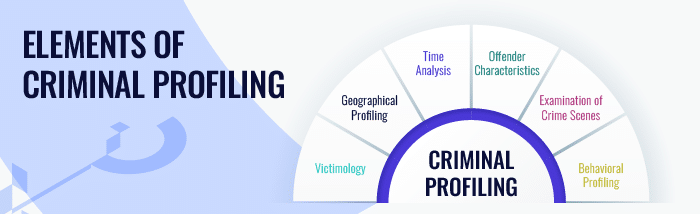
Key elements of criminal investigative analysis include:
- Victimology: Investigating the characteristics of victims to unravel potential connections with the offender and unveil any discernible patterns or links in victim selection.
- Geographical Profiling: Analyzing crime locations to unearth potential patterns, facilitating a more targeted approach in investigative endeavors.
- Time Analysis: Examining the temporal aspects of crimes to identify any recurring patterns or regularities in the offender’s conduct.
- Offender Characteristics: Formulating a detailed profile encompassing demographic information, potential motives, and other traits that can assist in narrowing down potential suspects.
- Examination of Crime Scenes: Scrutinizing crime scenes to pinpoint patterns, modus operandi (MO), and unique signatures that can provide valuable insights into the offender’s behavior.
- Behavioral Profiling: Crafting a comprehensive profile of the probable offender by analyzing behavioral traits, psychological characteristics, and motivations inferred from the crime scene details and available data.
How Can Investigative Analytics Accelerate Criminal Investigative Analysis?
Investigative Investigative analytics solutions are important tools that can assist investigators in accelerating criminal investigative analysis and help to uncover insights that would be difficult to attain through manual analysis. Investigative analytics solutions enable analysts and investigators to process and analyze large volumes of data from multiple sources and draw out actionable insights for investigations. Two capabilities in particular that can assist investigators:
- Processing and correlating data enables organizations to ingest their disparate and siloed data sets, aggregate them into a unified data pool, and align the data into a uniform format that can be easily queried. This allows investigators to analyze data from a wide variety of both structured and unstructured data sources, including criminal records, police reports, social media, and video footage, in one unified view.
- Visualization tools, such as timeline analysis, visual link analysis, and geospatial maps, can help investigators uncover connections and patterns from the available evidence, which they would otherwise have trouble finding.
Use Cases Where Investigative Analytics Can Help in Criminal Investigative Analysis
Criminal investigative analysis relies on analyzing investigation data in order to draw insights regarding the perpetrator of a crime. Investigative analytics solutions can be used to accelerate the process of criminal investigative analysis by:
- Finding hidden relations and connections between multiple victims in a case or investigation by using visual link analysis, timeline analysis, and geospatial analysis.
- Surfacing similar incidents or crimes in other jurisdictions that may be related to the investigation, by processing and correlating from diverse sources, making it easier to analyze data from other jurisdictions and agencies.
- Narrowing down the list of suspects by helping to determine which suspects to investigate. These tools can help to establish whether or not the suspect is connected to the time, place, and people involved in the crime.
Once a suspect or multiple suspects have been identified, investigative analytics can help to investigate them and determine whether the suspect worked with one or more accomplice(s) by analyzing their movement patterns, financial transactions, who they are communicating with, analyzing any suspicious behavior.
Click here to learn how law enforcement can use investigative analytics to accelerate investigations
Sources:
- https://www.apa.org/monitor/julaug04/criminal
- https://leb.fbi.gov/articles/featured-articles/criminal-investigative-analysis-practitioner-perspectives-part-one-of-four
- https://journalistsresource.org/criminal-justice/violent-media-real-world-behavior-historical-data-recent-trends/
- https://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1007/978-1-4614-5690-2_526